VLAN与三层交换机,了解后令人震撼
本文共 2851 字,大约阅读时间需要 9 分钟。
VLAN与三层交换机,了解后令人震撼
VLAN的概念及优势
分割广播域
物理分割和逻辑分割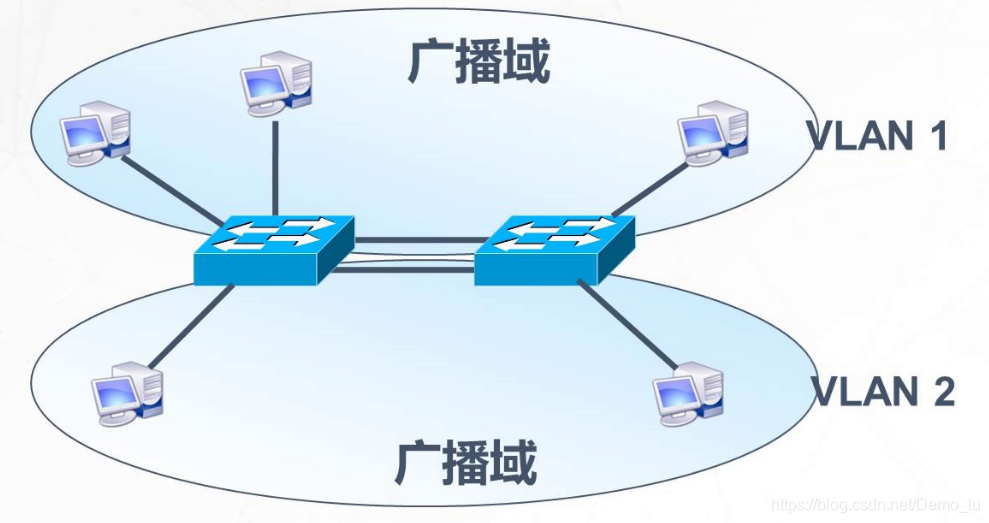 VLAN优势 可以控制广播 增强网络安全性 简化网络管理
VLAN优势 可以控制广播 增强网络安全性 简化网络管理 VLAN的种类
静态VLAN:基于端口划分静态VLAN
动态VLAN:基于MAC地址划分动态VLAN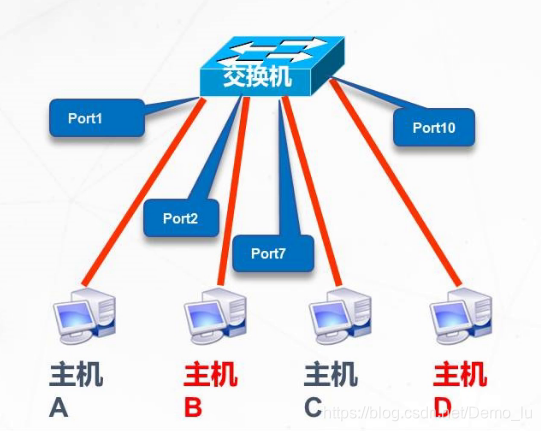
静态VLAN的配置
配置VLAN的相关命令
添加
[SW1]vlan 10 [SW1-vlan10]q批量添加
[SW1]vlan batch 20 30 40删除
[SW1]undo vlan 10#####将端口加入VLAN,Access口只能属于1个VLAN,一般用于连接计算机端口。
[Huawei]int e0/0/0 (进入接口模式) [Huawei-Ethernet0/0/0]port link-type access (定义二层端口为access模式) [Huawei-Ethernet0/0/0]port default vlan 10 (将端口加入到vlan中) [Huawei-Ethernet0/0/0]undo shutdown将端口从VLAN删除
[Huawei-Ethernet0/0/0] undo port default vlan [Huawei-Ethernet0/0/0] port link-type hybrid (将端口类型恢复成默认的hybrid) 查看当前端口模式、状态 [Huawei-Ethernet0/0/0] dis this同时将多个端口加入VLAN
[Huawei] port-group 1 (新增组1) [Huawei-port-group-1] group-member Ethernet 0/0/1 to Ethernet 0/0/20 (组1的成员是e0/0/1到e0/0/20) [Huawei-port-group-1] port link-type access [Huawei-port-group-1] port default vlan 30端口恢复默认配置,注意,执行完命令后,接口会被shut down
[Huawei] clear configuration interface e0/0/1查看指定VLAN信息
[Huawei] dis vlan 10####Trunk 类型端口:可以允许多个VLAN通过,可以接收和发送多个VLAN报文,一般用于交换机与交换机相关的接口。
[Huawei] int e0/0/0 [Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] port link-type trunk (定义二层端口模式) [Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 20 30 (配置Trunk 端口允许通过的vlan) [Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] undo shutdown 禁止Trunk传送某个VLAN的数据,删除这个VLAN [Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] undo port trunk allow -pass vlan 10心法口诀:
数据帧出口检查:查untag 表,有标时,脱标;无标时,查tag表,有则放通,无则丢掉 数据帧进口检查:先查有无标签,有标时,查tag表,有则放通,无标则丢弃; 无标时,打上PVID后,放通[Huawei] int e0/0/0 ###可理解成access 口
[Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] port link-type hybrid [Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] port hybrid pvid vlan 10 ###把Pvid 当成vlanid , 从PC到交换机进口的数据帧是没有标签的,所以要给数据帧打上标签再送进交换机[Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] port hybrid pvid vlan 10
###在untag 表里添加vlanid, 如果数据帧要从此接口出时就要先查untag 表,若发现有对应的vlanid 的标签就会脱掉此标签再发送出去 [Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] undo shutdown[Huawei] int e0/0/1 ###可理解成trunk 口
[Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] port link-type hybrid [Huawei-Etherent0/0/1] port hybrid tagged vlan 10 20 30 ###在tag 表里添加vlanid , 如果数据帧要从此接口出时就要先查 untag 表,如没有会再查tag 表,若发现有对应的vlanid 的标签就会放通,否则丢掉 [Huawei-Etherent0/0/1] undo shutdown[Huawei] int e0/0/2 ####上层接路由器配法
[Huawei-Etherent0/0/2] port link-type hybrid [Huawei-Etherent0/0/2] port hybrid untagged vlan 10 30 ###经过端口时脱去vlan10 30 标签 [Huawei-Etherent0/0/2 ] undo shutdown[Huawei] int e0/0/0
[Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] undo port default vlan ####初始化还原 [Huawei-Etherent0/0/0] port link-type hybrid ####将这个口变为hybrid 模式,华为交换机默认 hybrid口VLAN是逻辑隔离的虚拟局域网
VLAN能够隔离广播,提高安全性,简化管理 VLAN分为动态VLAN和静态VLAN 静态VLAN有两种配置方式:VLAN数据库和全局配置Trunk介绍与配置
access 接口类型是用于主机相连交换机,或者交换机和路由器相连 打上vlan标签
Trunk 交换机和交换机相连时的接口类型 识别vlan标签 Trunk 的作用 如何实现交换机之间的VLAN通信? 为每一个VLAN提供一条链路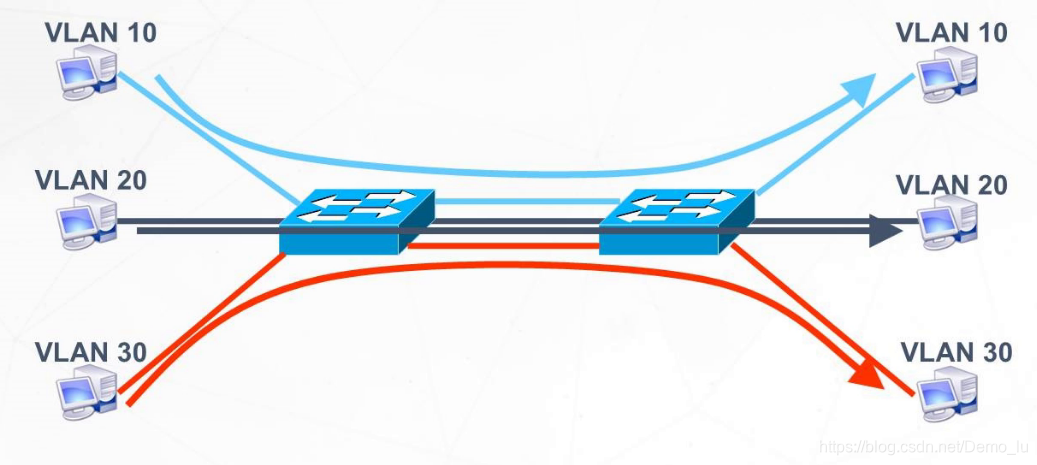
Trunk类型端口:可以允许多个VLAN通过,可以接收和发送多个VLAN报文,一般用于交换机与交换机相关的接口。
[Huawei]int e0/0/0
[Huawei-Ethernet0/0/0]port link三层交换技术
(一)、概念
1、使用三层交换机技术实现VLAN间通信 2、三层交换=二层交换+三层转发 (二)、传统的MLS2-1 1、三层转发过程中要重新封装2层 2、基于CEF的MLS转载地址:http://ykziz.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
navicat 系列软件一点击菜单栏就闪退
查看>>
navicat 自动关闭_干掉Navicat!MySQL官方客户端到底行不行?
查看>>
Navicat 设置时间默认值(当前最新时间)
查看>>
navicat 连接远程mysql
查看>>
navicat:2013-Lost connection to MySQL server at ‘reading initial communication packet解决方法
查看>>
Navicate for mysql 数据库设计-数据库分析
查看>>
Navicat下载和破解以及使用
查看>>
Navicat中怎样将SQLServer的表复制到MySql中
查看>>
navicat创建连接 2002-can‘t connect to server on localhost(10061)且mysql服务已启动问题
查看>>
Navicat可视化界面导入SQL文件生成数据库表
查看>>
Navicat向sqlserver中插入数据时提示:当 IDENTITY_INSERT 设置为 OFF 时,不能向表中的标识列插入显式值
查看>>
Navicat因导入的sql文件中时间数据类型有参数而报错的原因(例:datetime(3))
查看>>
Navicat如何连接MySQL
查看>>
navicat导入.sql文件出错2006- MySQLserver has gone away
查看>>
Navicat导入海量Excel数据到数据库(简易介绍)
查看>>
Navicat工具Oracle数据库复制 or 备用、恢复功能(评论都在谈论需要教)
查看>>
navicat工具查看MySQL数据库_表占用容量_占用空间是多少MB---Linux工作笔记048
查看>>
navicat怎么导出和导入数据表
查看>>
Navicat报错connection is being used
查看>>
Navicat报错:1045-Access denied for user root@localhost(using passwordYES)
查看>>